|
Dielectric pads are simple pouches containing a highly conductive material that are placed between the patient and the receiver coil to reduce dielectric artifacts. The simplest pads contain a dilute solution or gel containing manganese chloride. More complex solid pads contain suspensions of metal (primarily barium and calcium) titanates in deuterated or protonated water.
|
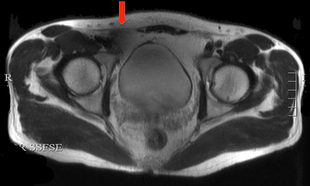
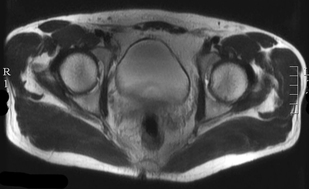
The effects of dielectric pads are several: 1) they provide improved impedance-matching for propagation of the B1 magnetic field; 2) displacement currents in the pad produce a secondary local RF field which augments the applied B1 field, and 3) the pads make the shape of the head or abdomen more spherical, thus reducing RF inhomogeneity effects intrinsic in elliptical geometry. Examples of the use of dielectric pads to reduce artifacts on pelvic MRI at 3T are shown below.
In our earliest 3T systems from 10-15 years ago, we used dielectric pads routinely for clinical imaging to improve B1 uniformity. Our modern 3T scanners employ dual RF technology, in which two separate sources with adjustable phase shifts are used transmit the RF-field. This technology has remarkably reduced image inhomogeneity effects and as such we no longer use dielectric pads. Nevertheless, some 3T sites still use these pads, and they are routinely used with 7.0T and 9.4T scanners.
Advanced Discussion (show/hide)»
No supplementary material yet. Check back soon.
References
Sled JG, Pike GB. Standing-wave and RF penetration artifacts caused by elliptic geometry: an electrodynamic analysis of MRI. IEEE Trans Med Imag 1998; 17: 653-662.
Webb AG. Dielectric materials in magnetic resonance, Concepts Magn Reson 2011; 38A:148-184.
Yang QX. Mao W, Wang J et al. Manipulation of Image Intensity Distribution at 7.0: Passive RF Shimming and Focusing With Dielectric Materials. J Magn Reson Imaging 2006;24:197–202.
Yang QX, Wang J, Wang J, et al. Reducing SAR and enhancing cerebral signal-to-noise ratio with high permittivity padding at 3T. Magn Reson Med 2011; 65:358-362
Sled JG, Pike GB. Standing-wave and RF penetration artifacts caused by elliptic geometry: an electrodynamic analysis of MRI. IEEE Trans Med Imag 1998; 17: 653-662.
Webb AG. Dielectric materials in magnetic resonance, Concepts Magn Reson 2011; 38A:148-184.
Yang QX. Mao W, Wang J et al. Manipulation of Image Intensity Distribution at 7.0: Passive RF Shimming and Focusing With Dielectric Materials. J Magn Reson Imaging 2006;24:197–202.
Yang QX, Wang J, Wang J, et al. Reducing SAR and enhancing cerebral signal-to-noise ratio with high permittivity padding at 3T. Magn Reson Med 2011; 65:358-362
Related Questions
What is the dielectric artifact?
What is the dielectric artifact?